Far-right in Germany & Brexit - Sophoz News
What are the causes and consequences of the rise of the far-right in Germany and what are the consequences of the Brexit in the UK
The rise of the far-right in Germany
Introduction
The far-right uprising in Germany in 2023 can be understood by examining the rise of the Alternative for Germany (AfD) party and the broader far-right movement in the country. Here are the key points to contextualize the uprising:
During the eurozone crisis, the AfD was founded in 2013 as an anti-euro party. Its initial focus was on economic issues, particularly advocating for Germany to leave the European Union's currency union or abolish it altogether. However, the party later shifted to the right during Europe's migration crisis in 2015, criticizing Chancellor Angela Merkel's open-door policy and gaining support as the only party to do so.
Germany's problem with right-wing extremism is evident in the AfD's success as the parliamentary arm of the broader far-right movement. The party commands around 15 percent of the vote nationwide and is the most significant electoral force in some regions. For a decade, the AfD has significantly shifted the country's politics to the right.
The AfD's rise can be attributed to various factors, including its aggressive anti-migrant stance, dissatisfaction with the political establishment, and concerns about economic issues, such as the cost of the Green Transition and inflation. The party has tapped into anxieties about Germany's future and attracted support from those who feel unsafe with rising migration, disagree with government policies, and fear the impact of climate plans on their way of life.
The AfD's success has led to debates about the implications for Germany's future. The rise of far-right parties, even if they do not capture a majority of the vote, can influence mainstream parties to adopt elements of their platforms. This phenomenon has been observed in Europe, where far-right parties have pushed mainstream parties to adopt more right-wing policies, particularly immigration, and integration. The influence of the far right can shape policy and drive polarization within the political system.
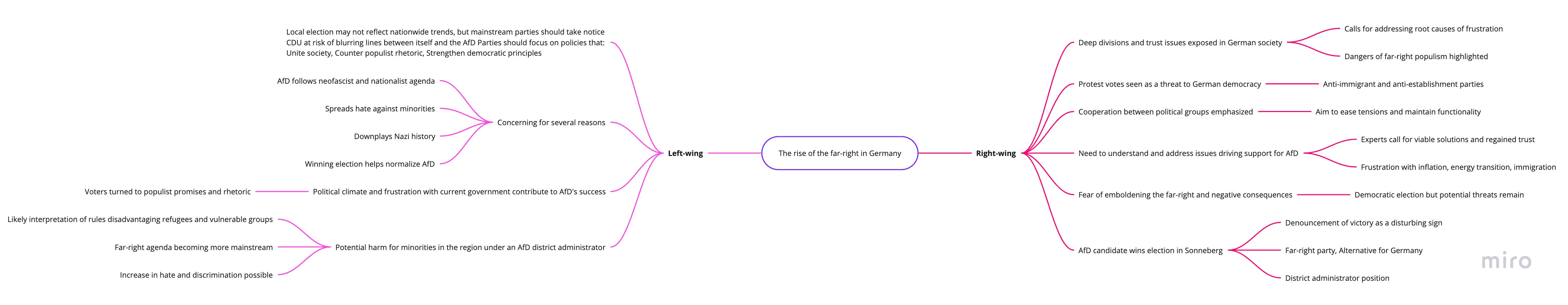
On June 25th of 2023, the AFD party won for the first time a local election and will lead the landkreis (district) of Sonneberg in Thuringia. This has brought back the debate over the uprise of the far right in Germany.
Right-wing
A candidate from the far-right Alternative for Germany (AfD) party has won the election to become district administrator in Sonneberg, a rural area in eastern Germany. Several politicians have denounced the AfD candidate's victory as a disturbing sign.
However, some argue that more needs to be done to understand and address the issues that drive people to vote for the AfD. Some experts say the AfD's rise reflects widespread frustration with issues like inflation, the energy transition, and immigration. They say political leaders must regain trust and offer viable solutions for those who vote out of protest.
Many leaders worry that the AfD victory could embolden the far-right, with possible negative consequences. However, they stress that the election was democratic. They hope that cooperation between political groups will ease tensions and maintain functionality in the district administration. Still, some remain concerned that protest votes for anti-immigrant and anti-establishment parties pose a threat to Germany's democracy.
Overall, the AfD win has exposed deep divisions and trust issues within German society. It has prompted warnings of the dangers of far-right populism and radicalization but also calls for political leaders to address the root causes behind citizens' frustrations and discontent.
Left-wing
The AfD, a far-right party, has won a local election for the position of district administrator in Sonneberg, Germany, for the first time. This is concerning for several reasons:
The AfD in Thuringia, led by Bjoern Hoecke, follows a neofascist and nationalist agenda. It spreads hate against minorities and downplays Nazi history. Winning this election helps normalize the AfD.
The overall political climate and frustration with the current government have helped the AfD. Many voters turned to populist promises and rhetoric.
For minorities in the region, an AfD district administrator can do a lot of harm. The AfD will likely interpret rules in a way that disadvantages refugees and vulnerable groups. The far-right agenda will become more mainstream. Hate and discrimination may increase.
While this local election may not reflect nationwide trends, mainstream parties should take notice. The CDU, in particular, risks damaging democracy by blurring the lines between itself and the AfD. Instead, parties should focus on policies that unite society, counter populist rhetoric and strengthen democratic principles.
Mind map recap
Brexit consequences

Introduction
Following extensive negotiations, the UK and the EU managed to reach a Trade and Cooperation Agreement on December 24, 2020, which outlined the framework for their future economic and political cooperation. This agreement covers various areas such as trade, security, fisheries, and data sharing.
In 2023, the relationship between the UK and the EU continues to evolve. Trade between the two entities has been affected by the new arrangements, with businesses adjusting to new customs procedures and regulatory frameworks. Some sectors, such as fishing, have experienced specific challenges due to changes in access to waters and fishing quotas.
Politically, the Brexit process has had a significant impact on the UK. The country has experienced internal debates and divisions over issues such as sovereignty, immigration, and the economic consequences of Brexit. The political landscape has also seen changes, with the Conservative Party, which led the Brexit campaign, facing both challenges and opportunities in its post-Brexit governance.
Overall, the Brexit process in 2023 is characterized by a period of adjustment and adaptation for both the UK and the EU. The full implications and long-term effects of Brexit are still unfolding, as both sides continue to navigate their new relationship and address the challenges and opportunities that arise.
Today two main ideas are implanted in the UK. On the one hand, those who thought Brexit allowed the UK to maintain its sovereignty and independence while helping them to make their own decision in immigration for example.
On the other hand, we have those who thought Brexit was a mess and destroy the competitiveness of the UK while they all achieved after Brexit could have been done as a member of the UE while profiting from all the benefits of the organization.
Pro Brexit
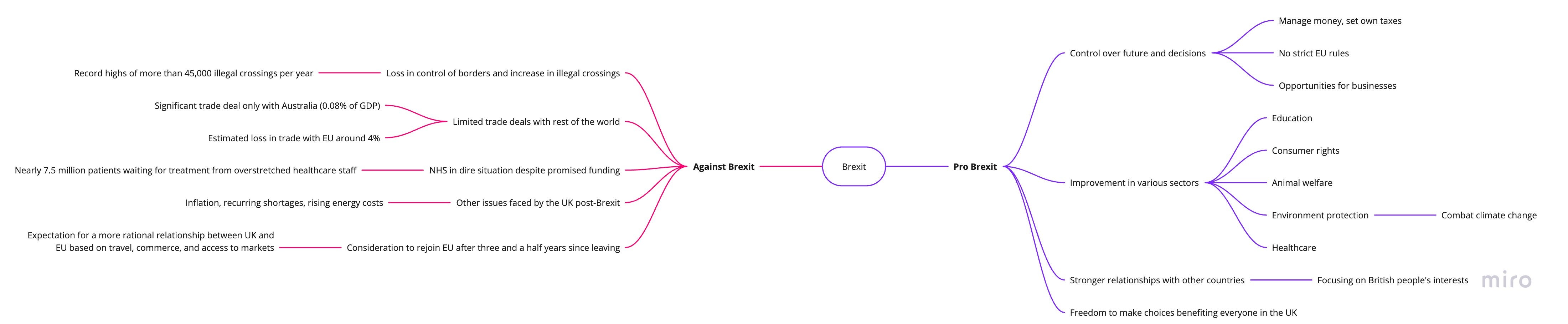
Brexit means that the UK is now in control of its own future and can make decisions based on what's best for its people. This includes managing our money and setting our own taxes, without following strict EU rules. We can also create new opportunities for businesses to grow and innovate globally.
Being independent also allows us to improve things like education, healthcare, consumer rights, and animal welfare. We can do more to protect the environment and meet our commitments to combat climate change.
Leaving the EU has given us a chance to build stronger relationships with other countries around the world, focusing on what's important to the British people. Overall, Brexit gives us more freedom to make choices that benefit everyone in the UK.
Against Brexit
Seven years after the UK voted to leave the European Union, the country has seen little to no of the benefits promised by Brexiteers. The UK was supposed to gain control of its borders and end the free movement of people within the Schengen Area. However, illegal crossings of the Channel have reached record highs of more than 45,000 per year. The country was also supposed to benefit from increased trade with the rest of the world. Yet, the only significant trade deal the UK has managed to negotiate is with Australia, which accounts for just 0.08% of the UK's GDP. The loss in trade with the European Union, which the UK left three and a half years ago, is estimated to be around 4%. The NHS, which was promised 350 million pounds sterling per week by Brexiteers, is in a dire situation, with nearly 7.5 million patients waiting for treatment from overstretched healthcare staff. Other symbolic advancements include using more locally produced goods in certain restaurants and shops, and the country is in a difficult economic situation with inflation, recurring shortages, and rising energy costs. The UK, which voted to leave the EU three and a half years ago, is now considering rejoining the union. Professor Tony Travers, a political scientist, believes that while the UK and the EU need each other, the two parties will eventually build a more rational relationship based on travel, commerce, and access to markets. The current UK Prime Minister, Rishi Sunak, was a Brexiteer, but he has since softened his stance and is now closer to his European counterparts, particularly France, on issues such as illegal immigration.
Mind map recap
Side notes
Thanks for reading this post!! If you liked it, feel free to leave a comment, share it, or shoot us an email! See you next week